5 Key Differences Between Android & iOS Marketers Should Consider
Many of the clients Urban Airship works with deploy iOS apps as their first foray into mobile because, in the U.S., it often seems as though everyone has an iPhone. While iOS may seem like the predominant platform in the U.S., Android subscribers actually make up 53% of the smartphone market. As of January 2016, Apple came in second at 43%.
Globally, Android commands 84% of the smartphone subscriber market share. The users and their mobile habits are very different, however. Given that framework, the distinct differences between Android and iOS and how each impacts mobile engagement are worth considering regardless of audience location.

How Android and iOS Capabilities Differ
1. Branded control vs. open-source roots
Apple tightly controls most aspects of their branding, hardware and software. Apps are reviewed prior to acceptance into the App Store. Push notifications must abide by Apple’s rules. To ensure users get a consistent experience, Apple pushes operating system updates to users. Marketers have always needed to play by Apple’s rules and timelines to participate in iOS apps.
In contrast, Google Play apps and app listings can be updated at any point, without review. Android OEMs and cellular carrier partners push Android updates to users. Android may have a larger market share, but it remains fragmented across phone manufacturers such as Samsung, LG, Motorola and HTC.
This freedom extends to the customizable experience Android offers to end-users of the device as well. On Android, you can install apps from “unknown sources,” allowing user to install applications from outside Google’s app store.
2. Same notification, different results
The same push notification will probably yield different results with iOS and Android audiences.
Our Notification Response Rates Benchmark Report showed that iOS has lower direct open rates, but higher influenced open rates across verticals. One reason for this could be that iOS consumers may not easily find the Notification Center on their iPhones and probably miss some pushes, as only the most recent notification is displayed. Conversely, Android has higher direct open rates, which may be due to notifications being shown on the locked screen and remaining in the notification bar until cleared.
3. Android offers different, creative messaging formats
Android supports a number of push notification formats that are not replicated on iOS. Expanded message formats and custom layouts such as “big text,” “rich content” and “inbox style” are creative formats great for retailers, music and entertainment brands to use for experimentation.
4. Opt-in experience
The two OS’ have very different strategies when it comes to allowing users to choose their level of mobile engagement. Apple users are accustomed to choice: the prompt for opt into push notifications and location-based data. Marketers have responded by with a number of tactics to get the opt in.
When Android users download an app from the Google Play store, they are informed that “this app has access to” a number of types of personal data ranging from identity to location, camera, photos, contacts, device and app history, device ID and call information. By installing the app, the user is giving consent. This puts the onus on the marketer to craft a compelling value proposition for users to opt-in, even before the app is able to display its value.
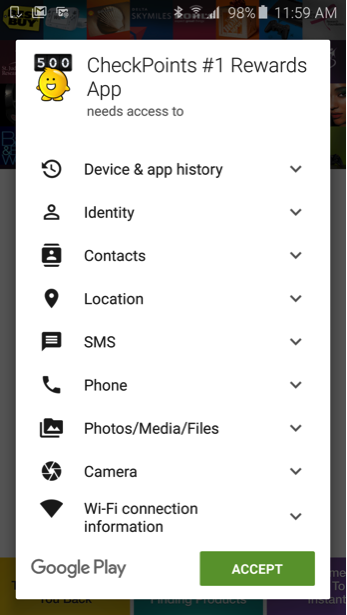
5. Audience Size or Engagement?
Deciding where to spend marketing dollars will likely come down to target audience, vertical and monetization goals. Comscore’s analysis of smartphone subscribers shows differences in how audiences engage with app content. In broad strokes: iOS users have higher levels of mobile engagement and actually spend more for apps. Apple has a stronghold on younger, professional and more affluent smartphone users in North America, China and Western Europe. Android is installed on more budget devices, has a larger, more disparate audience and strong market share in Asia, Latin America and Africa.
Next Step: Consider these 3 Factors
As mobile customer engagement strategies continue to mature, here are three key factors to consider when developing OS-specific plans:
- Android and iOS users behave differently — so make sure to assess app success by operating system and try different approaches for these audiences to increase response.
- Consider testing alternative creative, and day parting.
- With a cross-platform version of an app, make sure to spend when and where your users are more likely to engage.
For more about the differences between iOS and Android users, and get metrics to compare your own program against, download our Notification Response Rates Benchmark Report.
Alyssa Meritt leads the strategic consulting team at Urban Airship, which delivers tailored, digital marketing strategies to help clients increase mobile app engagement and grow business ROI. For more information about how they can help positively impact your mobile marketing success, please contact us.
Subscribe for updates
If the form doesn't render correctly, kindly disable the ad blocker on your browser and refresh the page.
